Machine learning is a way for computers to learn from data and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed for every task. Instead of following fixed rules written by a human, a machine learning system finds patterns, makes decisions, and gets better over time based on experience.
That definition sounds technical, but machine learning is already part of everyday life. You use it when Netflix recommends a movie, when Google Maps reroutes traffic, or when your email filters spam. This article explains machine learning in clear, human terms—without jargon overload—so you can understand what it is, how it works, and why it matters. stay with LearnAimind
Table of Contents
- What Is Machine Learning? (Simple Explanation)
- How Machine Learning Works in Real Life
- Machine Learning vs Traditional Programming
- Types of Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
- Common Machine Learning Algorithms
- Real-World Applications of Machine Learning
- Benefits and Limitations of Machine Learning
- Machine Learning, AI, and Deep Learning: What’s the Difference?
- Getting Started With Machine Learning
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Is Machine Learning? (Simple Explanation)
At its core, machine learning is about learning from examples.
Think about how humans learn:
- You see many examples
- You notice patterns
- You make better decisions next time
Machine learning follows the same idea, but with data instead of experiences.

A practical example
If you want a computer to recognize spam emails:
- Traditional approach: Write thousands of rules (keywords, sender addresses, formats)
- Machine learning approach: Show the system thousands of emails labeled “spam” or “not spam,” and let it learn the patterns on its own
Over time, the system becomes more accurate—even when spam tactics change.
How Machine Learning Works in Real Life
Machine learning systems usually follow this cycle:
1. Data collection
The system gathers data—numbers, text, images, or behavior logs.
2. Training
The model analyzes the data to find patterns and relationships.
3. Prediction or decision
Once trained, the model makes predictions on new, unseen data.
4. Improvement
As more data comes in, the system adjusts and improves.
This feedback loop is why machine learning systems feel “smart.” They adapt.
Machine Learning vs Traditional Programming
The difference between traditional software and machine learning is best shown visually.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Traditional Programming | Machine Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Rules | Written manually | Learned from data |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Adaptation | Needs reprogramming | Improves automatically |
| Best for | Clear logic problems | Pattern-based problems |
| Example | Calculator | Recommendation engine |
Traditional programming works well when rules are clear. Machine learning shines when rules are messy, hidden, or constantly changing.
Types of Machine Learning
Not all machine learning works the same way. There are three main types, each used for different problems.
Supervised Learning
What it is
The system learns from labeled data—data that already has correct answers.
Example
- Input: House size, location, age
- Output: House price
The model learns the relationship between inputs and outputs.
Common use cases
- Email spam detection
- Credit scoring
- Medical diagnosis
- Image classification
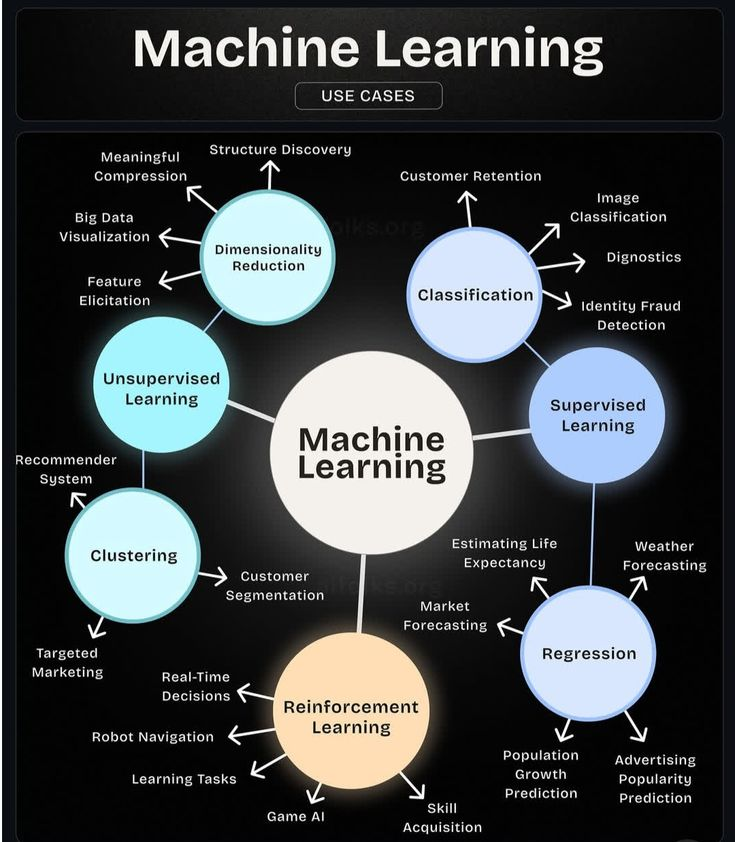
Unsupervised Learning
What it is
The system works with unlabeled data and looks for structure on its own.
Example
An online store groups customers based on buying behavior without knowing the groups in advance.
Common use cases
- Customer segmentation
- Market basket analysis
- Anomaly detection
- Topic modeling
Reinforcement Learning
What it is
The system learns by trial and error, receiving rewards or penalties.
Example
A self-driving car learns how to navigate roads by testing actions and learning from outcomes.
Common use cases
- Robotics
- Game AI
- Traffic signal optimization
- Recommendation tuning
Common Machine Learning Algorithms
You don’t need to be a data scientist to understand the big ideas behind popular algorithms.
Popular algorithms explained simply
| Algorithm | What It Does Well |
|---|---|
| Linear Regression | Predicts numbers based on trends |
| Logistic Regression | Handles yes/no decisions |
| Decision Trees | Makes rule-based decisions |
| Random Forest | Combines many decision trees |
| Support Vector Machines | Separates complex data |
| K-Means Clustering | Groups similar data points |
| Neural Networks | Handles images, speech, text |
Each algorithm is a tool. Choosing the right one depends on the problem, data size, and accuracy needs.
Real-World Applications of Machine Learning
Machine learning isn’t experimental anymore. It’s embedded in daily tools and major industries.
Healthcare
- Disease prediction
- Medical image analysis
- Drug discovery
- Patient risk assessment
Finance
- Fraud detection
- Credit scoring
- Algorithmic trading
- Risk management
Marketing and Sales
- Personalized recommendations
- Customer behavior prediction
- Dynamic pricing
- Ad targeting
Transportation
- Traffic prediction
- Route optimization
- Autonomous vehicles
- Ride-sharing matching
Everyday Technology
- Voice assistants
- Face recognition
- Search engines
- Smart home devices
Machine learning works quietly in the background, often unnoticed, but highly impactful.
Benefits and Limitations of Machine Learning
Like any technology, machine learning has strengths and weaknesses.
Benefits
- Handles large data efficiently
- Adapts to change
- Finds patterns humans miss
- Improves decision-making
- Automates repetitive tasks
Limitations
- Requires high-quality data
- Can inherit bias from data
- Often lacks transparency
- Needs computing power
- Not always accurate
Machine learning is powerful, but it’s not magic. Human judgment still matters.
Machine Learning, AI, and Deep Learning: What’s the Difference?
These terms are often mixed up, but they are not the same.
Simple hierarchy
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The broad goal of making machines act intelligently
- Machine Learning: A subset of AI focused on learning from data
- Deep Learning: A subset of machine learning using layered neural networks
Quick comparison table
| Term | Focus |
|---|---|
| AI | Mimicking human intelligence |
| Machine Learning | Learning patterns from data |
| Deep Learning | Learning complex patterns with neural networks |
All deep learning is machine learning, but not all machine learning is deep learning.
Getting Started With Machine Learning
If you’re curious about learning machine learning yourself, start small.
Practical steps
- Learn basic statistics and probability
- Understand how data works
- Explore Python and libraries like scikit-learn
- Practice with real datasets
- Focus on problem-solving, not buzzwords
You don’t need advanced math on day one. Many professionals start by solving simple, real problems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is machine learning in simple words?
Machine learning is when computers learn from data instead of following fixed rules.
Is machine learning the same as artificial intelligence?
No. Machine learning is a part of artificial intelligence, not the whole field.
Do I need coding skills to learn machine learning?
Basic coding helps, especially Python, but many tools now reduce technical barriers.
Can machine learning make mistakes?
Yes. Models depend on data quality and assumptions, so errors are possible.
Is machine learning used in small businesses?
Absolutely. It powers chatbots, analytics, recommendations, and automation tools.
Will machine learning replace human jobs?
It changes jobs more than it replaces them, often automating tasks rather than entire roles.
Final Thoughts
Machine learning is not a distant future concept—it’s a practical tool already shaping how we work, shop, travel, and communicate. Understanding what machine learning is helps you make better decisions, whether you’re a business owner, developer, student, or curious reader.
You don’t need to master algorithms to benefit from it. You just need to understand how learning from data is changing the rules of technology—and how you can use it wisely.